Buttigieg's health care plan would save money while Warren and Sanders plans would cost trillions, analysis finds
This post has been updated with comment from the Sanders campaign.
Health care has been a contentious topic among the Democratic presidential candidates: Sens. Bernie Sanders (I-VT) and Elizabeth Warren (D-MA) support Medicare for All while Mayor Pete Buttigieg (D-IN) and former Vice President Joe Biden offer alternatives to universal health care.
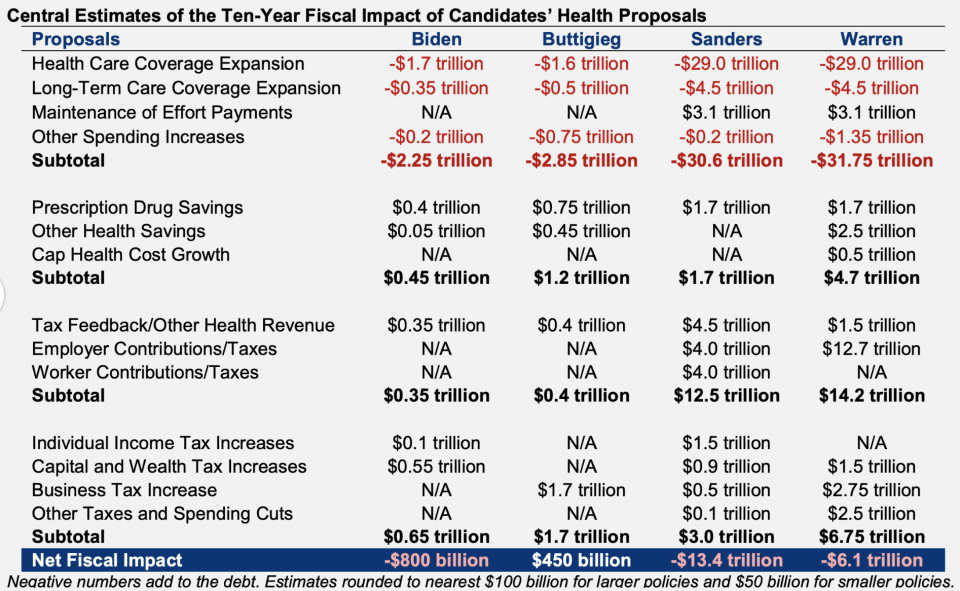
A new analysis from the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget (CRFB) took a look at the different plans and found that while each proposal would reduce the number of uninsured Americans, the least costly would be Buttigieg’s plan.
“Mayor Buttigieg’s plan would reduce deficits by $450 billion,” according to CFRB, adding that the policy would also “increase gross spending by $2.85 trillion, reduce costs by $1.2 trillion, and raise $2.1 trillion through direct and additional offsets.”
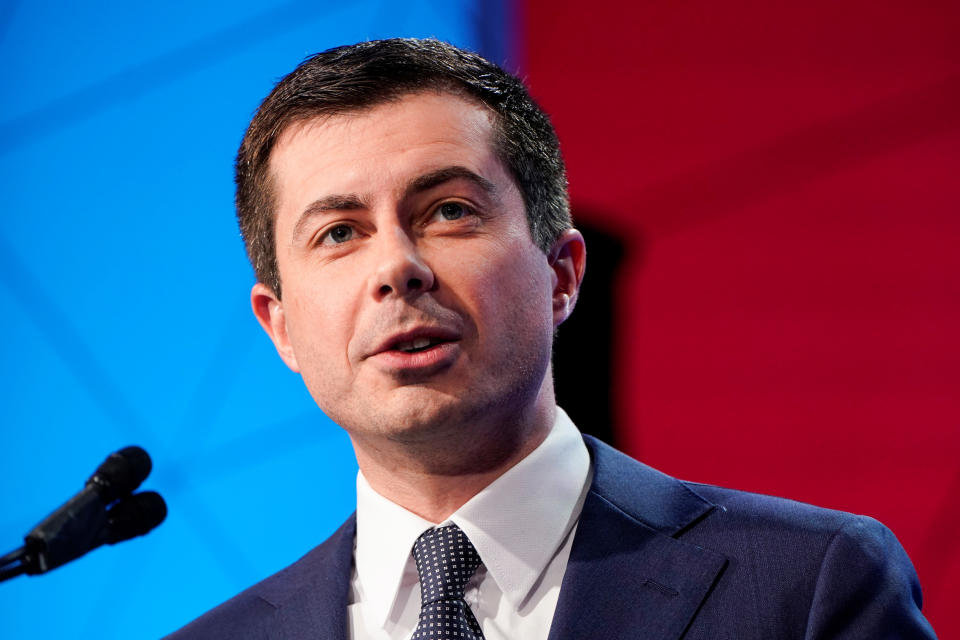
Through Buttigieg’s Medicare for All Who Want It plan, everyone would automatically be involved in universal health care coverage for those who are eligible. The policy would also expand premium subsidies for low-income individuals, cap out-of-pocket costs for seniors on Medicare, and limit what health care providers change for out-of-network care at double what Medicare pays for the same service. At the same time, those who still want to stay on private insurance can do so.
“This is how public alternatives work,” Buttigieg said. “They create a public alternative that the private sector is then forced to compete with.
CRFB estimated that the Indiana mayor’s plan would reduce the number of uninsured by between 20 to 30 million “by improving affordability and implementing auto-enrollment as well as retroactively enrolling and charging premiums to those who lack coverage.”

‘Building on Obamacare’
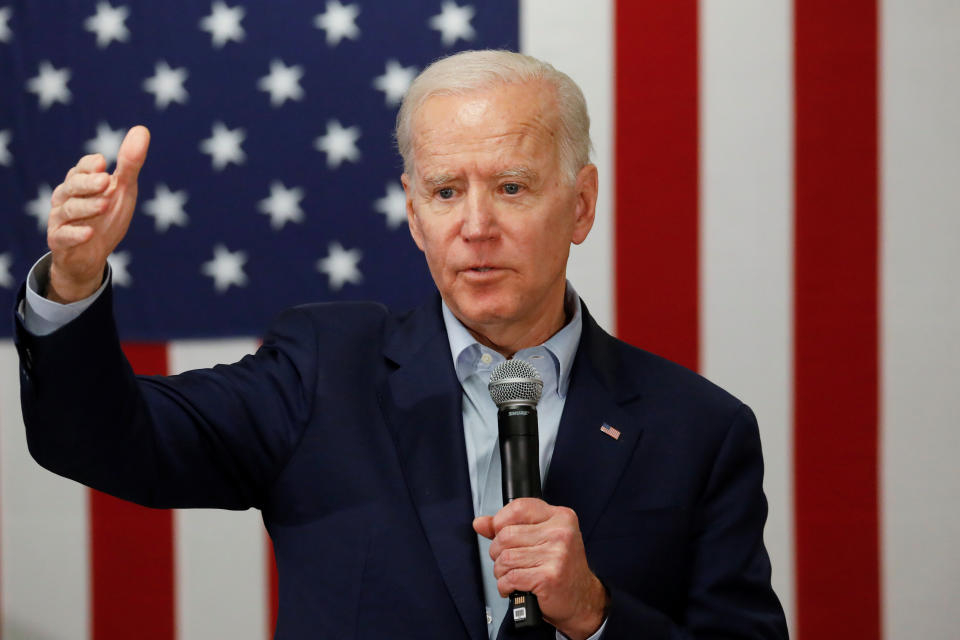
Joe Biden’s health care plan, described as “building on Obamacare,” has an estimated gross cost of $2.25 trillion and would add $800 billion to deficits over 10 years. The CRFB also found that “it would reduce costs by $450 billion” and “raise $1 trillion through direct and additional offsets.”
Biden’s plan would reduce the number of uninsured by 15 to 20 million Americans and reduce national health expenditures by 1%.
Some of his biggest revenue drivers in his plan include coverage expansion revenue feedback, which would create a public option, and end deductibility of prescription drug advertising. Additionally, his capital gains tax and “tax at death” would generate $550 billion.

‘Federal health expenditures would increase somewhat more’
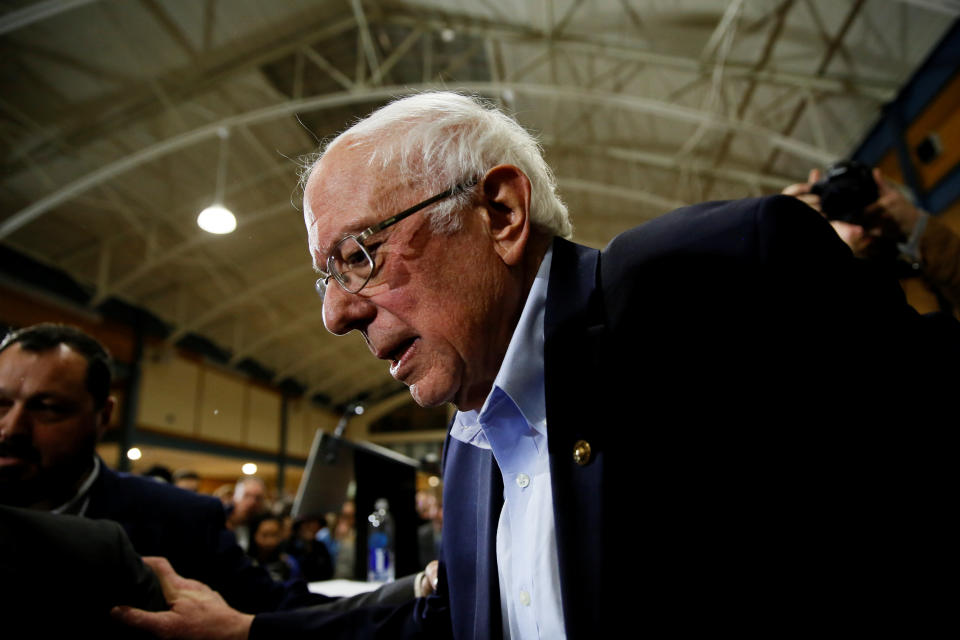
Sen. Sanders, one of the original proponents of Medicare for All, has a plan that’s projected to add $13.4 trillion to deficits over a decade at a gross cost of $30.6 trillion. It would also raise $12.5 trillion in revenue through direct offsets and raise another $3 trillion through additional offsets.
His proposals to eliminate medical debt would cost $100 billion and would raise $1.7 trillion by reducing the costs of prescription drugs. To generate more money for the plan, Sanders would establish a 4% income surtax (projected to raise $4 trillion) and 7.5% employer payroll tax (estimated $4 trillion added). One significant cost in his plan, though, is offering universal long-term care — which would cost $29 trillion.
"The reality is that Medicare for All will save American families thousands of dollars a year because they will no longer be paying premiums, deductibles and co-payments to greedy private health insurance companies,” Warren Gunnels, senior advisor for the Sanders campaign, told Yahoo Finance in a statement.
“If every major country on earth can guarantee health care to all and achieve better health outcomes, while spending substantially less per capita than we do, it is absurd for anyone to suggest that the United States of America cannot do the same."
Overall, between 2021 to 2030, the CFRB estimated that Sanders’ plan would increase national health expenditures by 6%, “meaning that federal health expenditures would increase somewhat more than non-federal health spending would fall.”

‘Magical math’ or ‘the biggest middle class tax cut ever’?
Sen. Warren’s plan closely resembles Sanders’ in terms of cost. She stated her plan would cost $20.5 trillion in federal spending over a decade. CFRB found that the plan “would add $6.1 trillion to deficits over ten years under our central estimate.”
Experts disagree over the cost of Warren’s numbers, with one calling it “magical math” and another referring to Warren’s plan as “the biggest middle class tax cut ever.”
According to CRFB, the plan would increase gross spending by $31.75 trillion, reduce costs by $4.7 trillion, raise $14.2 trillion in revenue through direct offsets, and raise another $6.75 trillion through additional offsets. Her health care plan is estimated to increase costs by about 3%, but “the magnitude of these increases would decline over time.”
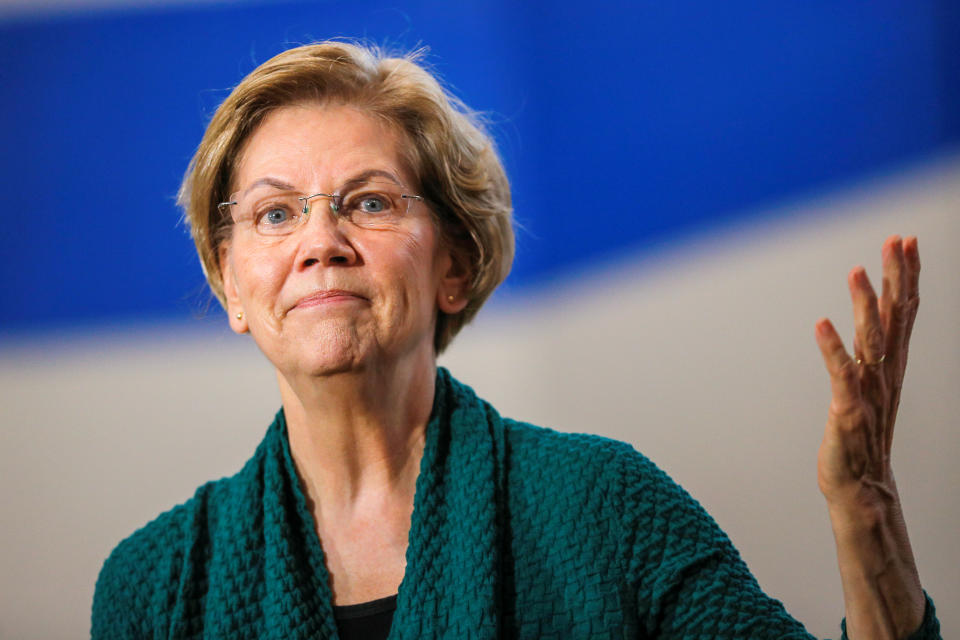

A major way to fund the plan would be through tax reform. By essentially eliminating tax breaks with private health insurers and requiring employers to contribute to her Medicare for All, she’s projected to generate an estimated $14.2 trillion. Other means of generating revenue for her plan include her wealth tax and a tax on bonds, stocks, and derivatives.
Both the Warren and Sanders plans would reduce the number of uninsured Americans by 30 to 35 million and “nearly eliminate” average premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
Adriana is an associate editor for Yahoo Finance. She can be reached at [email protected]. Follow her on Twitter @adrianambells.
READ MORE:
Follow Yahoo Finance on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, Flipboard, SmartNews, LinkedIn, YouTube, and reddit.
